The influence of active learning and submicrorepresentations on 14-year-old students understanding of the alkaline earth metal concepts Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
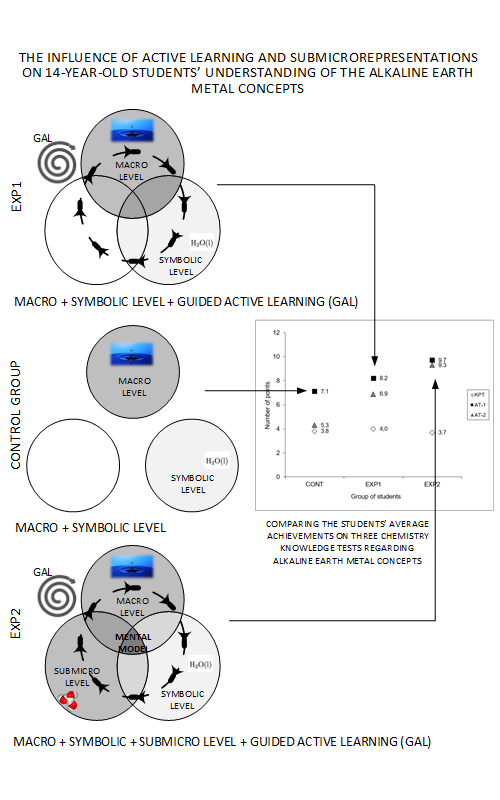
This study aimed to examine the impact of two different approaches on students understanding of selected chemical concepts. The first treatment group was taught by a method comprising guided active learning demonstrations, and the second treatment group was exposed to guided active learning demonstrations with explanations at the submicroscopic level. In a control group, the selected topic was taught without guided active learning demonstrations and without explanations at the submicroscopic level. The instruments used in this research included the test of logical thinking (TOLT), knowledge pre-test (KPT), two achievement tests (AT-1 and AT-2) and a questionnaire for students. One hundred and seventy-one students (average age 13.9 years) participated in the study. The results indicate that both approaches (i.e., guided active learning demonstrations and guided active learning demonstrations with explanations at submicroscopic level) are more effective than only symbolic teaching. It can be concluded from the results that students knowledge, obtained by either method that includes guided active learning, is retained in the students long-term memory. Some suggestions for implications for the primary science curriculum are also discussed.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
References
A. H. Johnstone, Sch. Sci. Rev. 64 (1982) 377
D. Gabel, J. Chem. Educ. 76 (1999) 548 (https://doi.org/10.1021/ed076p548)
D. F. Treagust, A. G. Harrison, G. J. Venville, J. Sci. Teacher Educ. 9 (1998) 85 (https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009423030880)
H. K.Wu, J. S. Krajcik, E. Soloway, J. Sci. Teacher Educ. 38 (2001) 821 (https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.1033)
A. G. Harrison, D. F. Treagust, Chemical Education: Towards Research-Based Practice, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 2002, pp. 189–212 (https://www.academia.edu/5488505/Chemical_education_towards_research_based_practice_science_technology)
D. F. Treagust, G. Chittleborough, T. Mamiala, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 25 (2003) 1353 (https://doi.org/10.1080/0950069032000070306)
J. E. Upahi, U. Ramnarain, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 20 (2019) 146 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RP00191J)
R. M. Kelly, L. L. Jones, J. Chem. Educ. 85 (2008) 303 (https://doi.org/10.1021/ed085p303)
I. Devetak, S. A. Glažar, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 32 (2010) 1561 (https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690903150609)
J. M. Nyachwaya, M. Gillaspie, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 17 (2016) 58 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RP00140D)
N. Becker, C. Stanford, M. Towns, R. Cole, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 16 (2015) 769 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RP00064E)
D. D. Rodić, T. N. Rončević, M. D. Segedinac, Acta Chim. Slov. 65 (2018) 394 (http://dx.doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2017.4139)
L. Dee Fink, Creating significant learning experiences: An integrated approach to designing college courses. Calif: Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, CA, 2003, pp. 102–154 (https://www.wiley.com/ensi/Creating+Significant+Learning+Experiences%3A+An+Integrated+Approach+to+Designing+College+Courses%2C+Revised+and+Updated-p-9781118416327)
K. L. Adams, J. A. Luft, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 13 (2018) 69
G. Papageorgiou, P. Johnson, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 27 (2005) 1299 (https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690500102698)
M. Stains, V. Talanquer, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 29 (2007) 643 (https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690600931129)
B. Davidowitz, G. Chittleborough, E. Murray, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 11 (2010) 154 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C005464J)
V. Talanquer, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 33 (2011) 179 (https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690903386435)
K. de Berg, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 13 (2012) 8 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C1RP90056K)
U. Ramnarain, U. A. Joseph, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 13 (2012) 462 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RP20071F)
K. S. Taber, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 14 (2013) 151 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RP00012E)
M. M. W. Cheng, J. K. Gilbert, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 39 (2017) 1173 (http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2017.1319989)
D. D. Trivić, V. D. Milanovič, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 83 (2018) 1177 (http://doi.org/10.2298/JSC171220055T)
G. Chittleborough, Learning with Understanding in the Chemistry Classroom, Springer, Dordrecht, 2014, pp. 25–40 (https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9789400743656)
I. Devetak, J. Vogrinc, S. A. Glažar, Res. Sci. Educ. 39 (2009) 157 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-007-9077-2)
J. D. Bradley, M. Brand, G. G. Gerrans, S. Afr. J. Sci. Educ. 37 (1998) 85
N. Solsona, M. Izquierdo, M. O. De Jong, Int. J. Sci. Educ. 25 (2003) 3
E. Adadan, K. C. Trundle, K. E. Irving, J. Res. Sci. Teach. 47 (2010) 1004 (https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.20366)
A. L. Kerna, N. B. Woodb, G. H. Roehrigc, J. Nyachwayac, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 11 (2010) 165 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C005465H)
O. Lee, D. C. Eichinger, C. W. Anderson, G. D. Berkheimer, T. D. Blakeslee, J. Res. Sci. Teach. 30 (1993) 249 (https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.3660300304)
C. Bonwell, J. Eison, Active Learning: Creating Excitement in the Classroom, George Washington University, Washington, DC, 1991 (https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED336049)
J. S. Bruner, Harv. Educ. Rev. 31 (1961) 21
D. Muijs, D. Reynolds, Effective teaching: Evidence Based Practice, Sage Publications, London, 2017
P. A. Kirschner, J. Sweller, R. E. Clark, Educ. Psychol. 41 (2006) 75 (https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep4102_1)
P. H. Walton, Univ. Chem, Educ. 6 (2002) 22
G. Tsaparlis, Learning with Understanding in the Chemistry Classroom, Springer, Dordrecht, 2014, pp. 41–61 (https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9789400743656)
National Research Council, How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition, The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. 2000. pp. 3–23 (https://www.nap.edu/catalog/9853/how-people-learn-brain-mind-experience-and-school-expanded-edition)
R. Moreno, Instr. Sci. 32 (2004) 99 (https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRUC.0000021811.66966.1d)
L. Deslauriers, L. S. McCarty, K. Miller, K. Callaghan, G. Kestin, PNAS 116 (2019) 19251 (https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821936116)
K. G. Tobin, W. Capie, Educ. Psychol. Meas. 41 (1981) 413 (https://doi.org/10.1177/001316448104100220)
B. Marentič Požarnik, Psychology of learning and instruction, DZS, Ljubljana, 2000 (https://doi.org/10.4312/as.6.4.150-152) (in Slovenian)
V. M. Williamson, M. R. Abraham, J. Res. Sci. Teach. 32 (1995) 521 (https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.366032050843)
G. Chittleborough, D. F. Treagust, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 8 (2007) 274 (https://doi.org/10.1039/B6RP90035F)
J. S. Chall, The academic achievement challenge, Guilford Press, New York, 2000
D. Klahr, M. Nigam, Psychol. Sci. 15 (2004) 661 (https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0956-7976.2004.00737.x)
I. Devetak, S. A. Glažar, Facilitating effective student learning through teacher research and innovation, University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Education, Ljubljana,2010, pp. 399–
–414 (http://www.pef.uni-lj.si/ceps/knjiznica/doc/zuljan-vogrinc.pdf)
D. M. Bunce, D. Gabel, J. Res. Sci. Teach. 39 (2002) 911 (https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.10056).